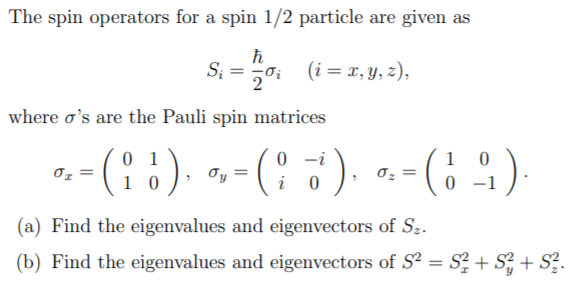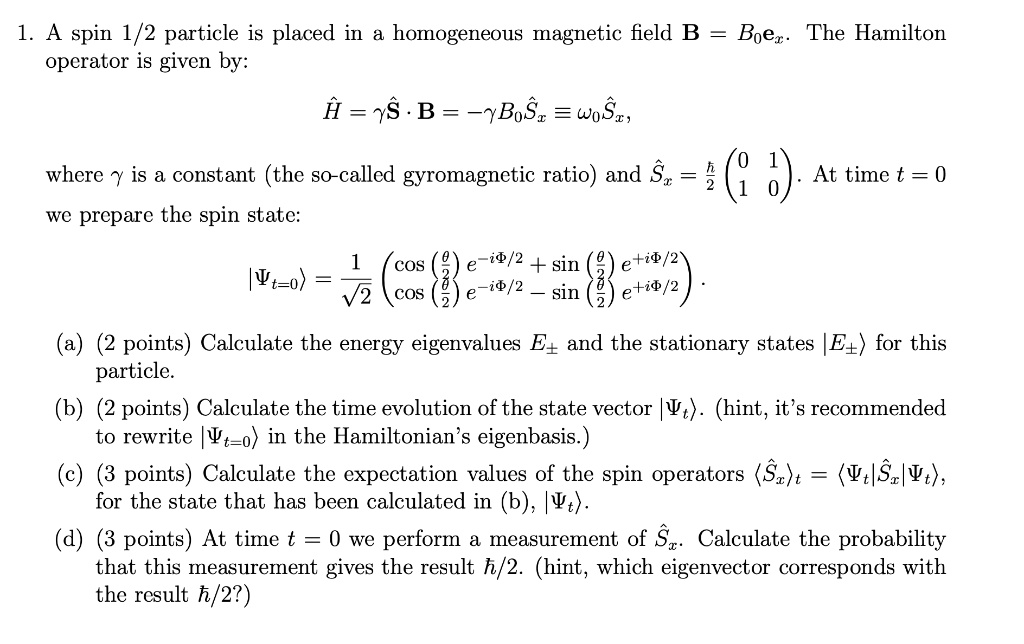
SOLVED: A spin 1/2 particle is placed in a homogeneous magnetic field B = Boex. The Hamiltonian operator is given by: H = yS · B = -BgS = woSx where y

SOLVED: Ladder Operators a) In the 2 basis set, the spin-1/2 operators can be written using the Pauli spin matrices: σx, σy, σz. Using these, S = (ħ/2)σ, etc. From the matrix
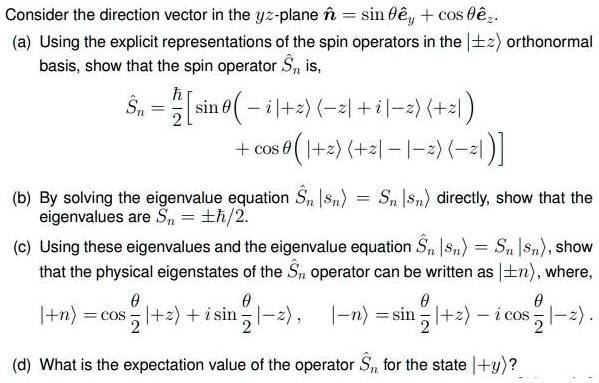
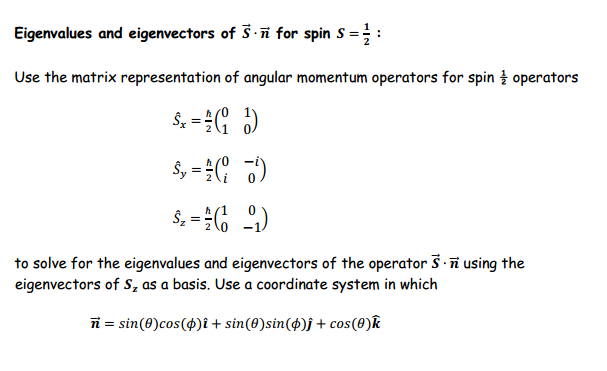
SOLVED: Consider the direction vector in the yz-plane n = sin θev + cos θe . (a) Using the explicit representations of the spin operators in the |-z) orthonormal basis, show that
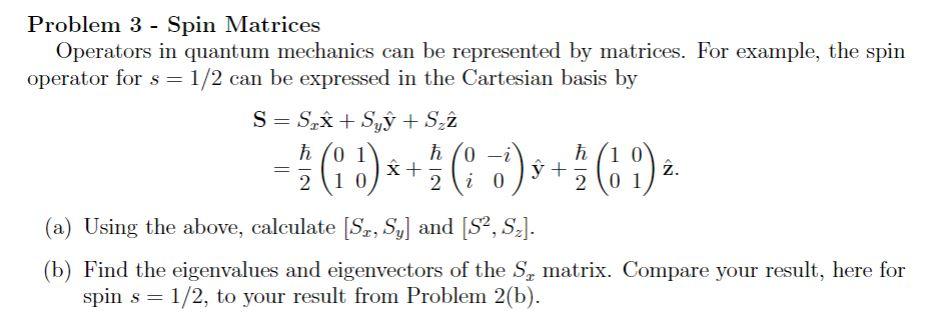
![SOLVED: The spin operators - S, S, and S - are very much like the angular momentum operators (L, L, and L) in that they obey the commutation relations: [S,S]=ihs, [S,S]=ihs, and [ SOLVED: The spin operators - S, S, and S - are very much like the angular momentum operators (L, L, and L) in that they obey the commutation relations: [S,S]=ihs, [S,S]=ihs, and [](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/10e346240a374097bc9ae3d169afe2ca.jpg)
SOLVED: The spin operators - S, S, and S - are very much like the angular momentum operators (L, L, and L) in that they obey the commutation relations: [S,S]=ihs, [S,S]=ihs, and [
Expected values of the magnetization spin operator O = I z + S z , with... | Download Scientific Diagram
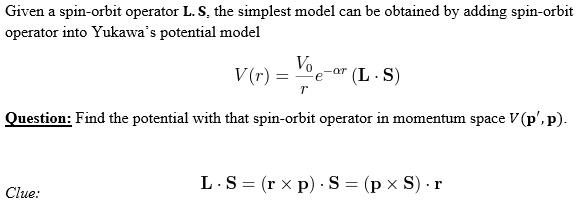
SOLVED: Given a spin-orbit operator L.S., the simplest model can be obtained by adding the spin-orbit operator into Yukawa's potential model: V(r) = e^(-ar) (L S) 7 Question: Find the potential with

Expectation value of the z− projection of the spin operator, < S z > as... | Download Scientific Diagram